The phenomenon of mentorship relationship mismatches represents one of the most significant challenges in professional development programs across organizations worldwide. Despite the widespread adoption of mentoring programs—with 84% of Fortune 500 companies implementing such initiatives—research reveals a troubling disconnect between program availability and actual effectiveness. Only 37% of professionals report genuinely benefiting from mentorship programs, while studies indicate that between 33% to 50% of mentoring relationships terminate prematurely before achieving their intended objectives. This comprehensive analysis examines the multifaceted nature of mentorship mismatches, exploring their underlying causes, manifestations, and profound impact on both individual career development and organizational success.mentoringcomplete+3
The Anatomy of Mentorship Relationship Failures
Communication Breakdowns: The Foundation of Dysfunction
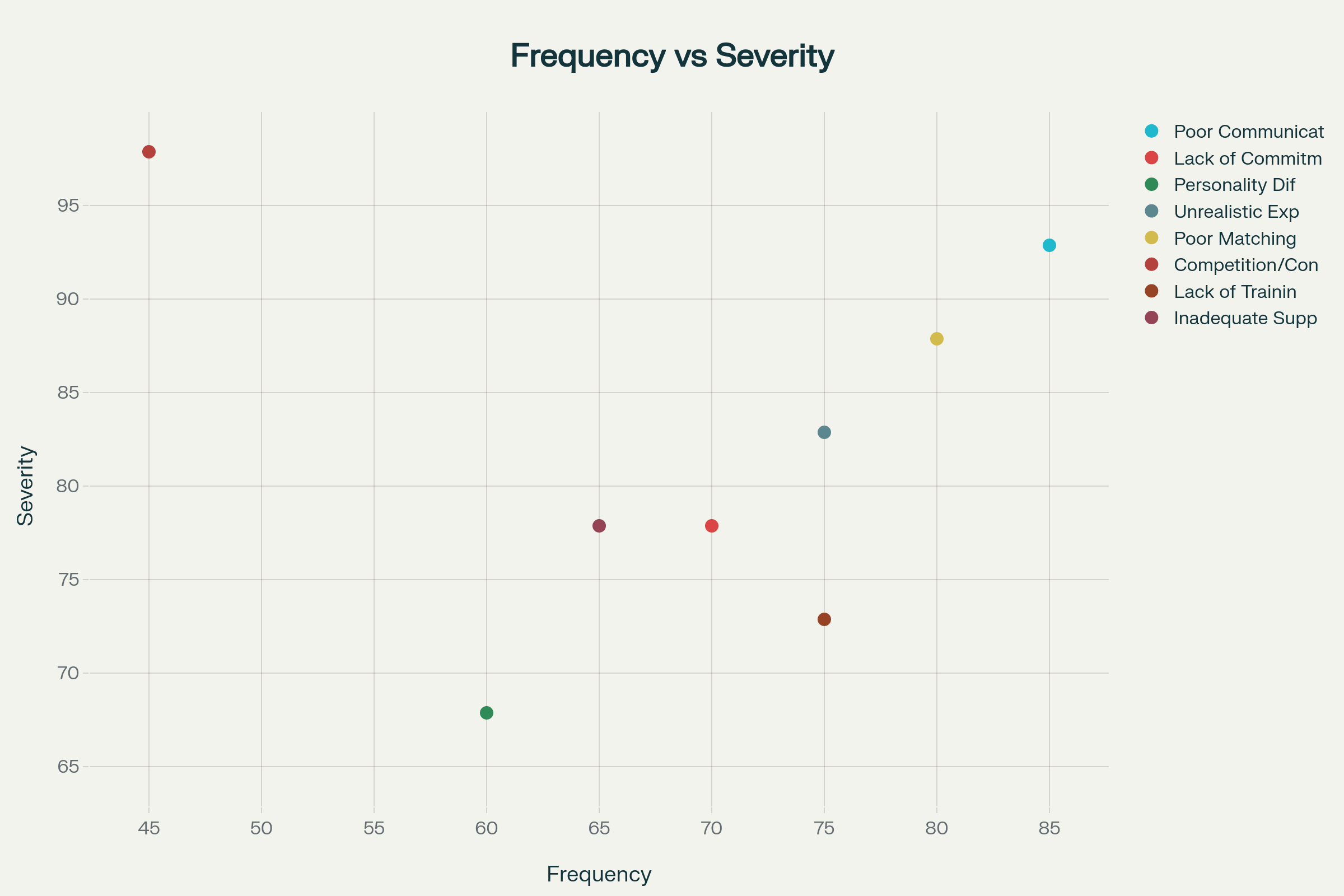
Poor communication emerges as the most pervasive and destructive factor in mentorship failures, affecting approximately 85% of unsuccessful relationships with a severity rating of 90%. Communication breakdowns manifest in multiple dimensions, ranging from fundamental listening deficits to more complex issues of expectation alignment. Research conducted across academic health centers reveals that failed mentoring relationships are consistently characterized by “poor communication, lack of commitment, personality differences, perceived (or real) competition, conflicts of interest, and the mentor’s lack of experience”.mentorcliq+2
The communication crisis in mentorship relationships often begins with misaligned expectations during the initial relationship formation phase. When mentors and mentees fail to establish clear parameters for their interaction—including meeting frequency, communication channels, goal-setting processes, and feedback mechanisms—the relationship becomes vulnerable to misunderstandings and frustration. A study examining graduate-level mentoring relationships found that “mentee discontent is typically caused by a lack of mentor knowledge or availability, lack of interpersonal skills, deceit, unequal treatment, interpersonal mismatch, and lack of career or emotional support”.lead-true+4
Categories and Types of Mentorship Relationship Mismatches
The digital age has introduced additional complexity to mentorship communication, with participants often struggling to establish effective virtual connection protocols. Organizations report that hybrid and remote mentoring arrangements, while offering geographic flexibility, can exacerbate communication challenges when proper technological frameworks and communication guidelines are not established.chronus+2
Personality and Values Misalignment: Deep-Level Incompatibilities
Beyond surface-level communication issues, research indicates that deep-level similarity between mentors and mentees significantly influences relationship quality, particularly in academic settings where the effect is considerably stronger than in workplace environments. The similarity-attraction paradigm suggests that individuals naturally gravitate toward and develop higher-quality relationships with those who share their fundamental values, attitudes, and beliefs.womentech+1
Personality clashes represent a particularly insidious form of mismatch because they often manifest gradually and can be difficult to address through conventional intervention strategies. Studies utilizing the Big Five personality framework reveal complex dynamics where certain trait combinations can either enhance or undermine mentoring effectiveness. For instance, research found that highly agreeable mentors, contrary to expectations, were sometimes associated with lower relationship quality because mentees perceived them as lacking clear direction and guidance.mentorloop+2
The challenge of personality misalignment is compounded by the fact that many organizations rely on surface-level demographic matching rather than deeper psychological compatibility assessments. Harvard Business Review research indicates that 71% of executives choose to mentor employees of their same gender or race, suggesting that demographic similarity is often prioritized over psychological or professional compatibility.tenthousandcoffees+1
Structural and Systemic Barriers
Organizational factors play a crucial role in mentorship success or failure, with inadequate program design and support structures contributing significantly to relationship breakdowns. Research identifies several systemic issues that create environments where mentorship mismatches are more likely to occur and persist. These include insufficient training programs, poor matching algorithms, lack of ongoing support, and absence of clear program objectives.chronus+2
The training deficit is particularly striking: studies show that only 33% of mentoring relationships succeed when no training is provided to either party. This success rate increases to 66% when mentors receive professional training, and reaches 90% when both mentors and mentees are properly prepared for their roles. These statistics underscore the critical importance of systematic preparation in preventing relationship failures.evidencebasedmentoring
Categorizing Mentorship Mismatches: A Comprehensive Framework
Surface-Level Mismatches
Surface-level mismatches encompass readily observable differences that can create initial barriers to relationship formation but are often surmountable with proper support and commitment. These include demographic disparities such as significant age gaps, cultural differences, and educational background variations. Professional mismatches in this category involve industry experience gaps, role level disparities, and skill set incompatibilities that, while challenging, can be addressed through structured learning approaches.tenthousandcoffees+3
Logistical surface-level mismatches have become increasingly relevant in the modern workplace, encompassing geographic distance, time zone conflicts, and technology platform preferences. While these practical barriers can be overcome through careful planning and technological solutions, they require deliberate organizational support to prevent them from undermining relationship development.chronus+1
Deep-Level Mismatches
Deep-level mismatches represent more fundamental incompatibilities that are often more difficult to resolve and can have lasting negative impacts on both participants. Values misalignment, including different work ethics, conflicting priorities, and divergent definitions of success, creates persistent tension that can undermine even well-intentioned mentoring efforts.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih+2
Personality-based deep-level mismatches involve fundamental differences in communication styles, risk tolerance, and learning preferences that can create ongoing friction. Goal misalignment represents another critical category, where mentors and mentees have incompatible objectives, different growth expectations, or conflicting timelines for achievement.womentech+3
Behavioral Mismatches
Behavioral mismatches manifest through actions and patterns of interaction that demonstrate incompatibility or dysfunction in the mentoring relationship. Communication behavioral issues include poor listening skills, inadequate feedback provision, dismissive attitudes, and mismatched communication frequency preferences.lead-true+3
Engagement behavioral mismatches involve low commitment levels, inconsistent participation, lack of preparation, and passive involvement from either party. These behaviors often signal deeper issues with motivation, time management, or understanding of mentoring role expectations.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih+3
Boundary-related behavioral mismatches represent some of the most serious relationship dysfunctions, including professional boundary violations, over-dependence, inappropriate personal sharing, and abuse of power dynamics. These issues can create lasting negative impacts that extend beyond the immediate mentoring relationship.mentorink+1
Systemic Mismatches
Systemic mismatches arise from organizational and structural factors that create environments where mentoring relationships cannot thrive regardless of individual participant qualities. Organizational systemic issues include lack of program support, unclear guidelines, inadequate training, and poor matching algorithms.chronus+3
Cultural systemic mismatches involve toxic workplace environments, lack of recognition for mentoring contributions, insufficient resource allocation, and poor overall program design. These factors create contexts where even well-matched and well-intentioned participants struggle to develop effective relationships.apa+1
Structural systemic mismatches encompass hierarchical conflicts, problematic reporting relationships, resource competition, and time allocation problems that create competing priorities and conflicting loyalties.eller.arizona+1
The Psychology of Toxic Mentorship
Frequency vs Severity of Mentorship Relationship Failure Factors
Identifying Toxic Mentoring Patterns
The concept of “mentorship malpractice” has emerged as a critical framework for understanding the most harmful forms of mentoring dysfunction. Research identifies three primary categories of active mentoring failures: hijackers who take credit for mentee achievements, exploiters who use mentees for self-serving tasks while providing little value in return, and possessors who prevent mentees from seeking alternative guidance or opportunities.mentorink+1
Passive mentoring failures can be equally damaging though less obvious, including bottlenecks who fail to provide timely feedback, country clubbers who avoid difficult conversations, and world travelers who are too consumed with their own schedules to provide adequate attention. These patterns create environments where mentees may actually be worse off than if they had no mentor at all.linkedin+3
The psychological impact of toxic mentorship extends beyond immediate professional consequences, often resulting in decreased job satisfaction, heightened burnout, severe loss of confidence, and long-term reluctance to seek mentoring relationships. Studies indicate that mentees subjected to exploitation or neglect frequently lose faith in their own abilities and in the concept of mentorship itself, creating lasting barriers to professional development.togetherplatform+3
Red Flags and Warning Signs
Research has identified numerous warning signs that indicate developing or existing mentorship toxicity. These include mentors who consistently fail to value mentee input, demonstrate poor listening skills, insist on always knowing best, take credit for mentee accomplishments, fail to provide constructive feedback, and leave mentees feeling drained after interactions.linkedin+2
From the mentee perspective, warning signs include lack of initiative, failure to implement advice, consistent ingratitude, entitled attitudes, and unwillingness to take accountability for their own development. The presence of these behaviors often indicates fundamental misalignment in understanding mentoring roles and responsibilities.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih+1
Organizational Impact and Consequences
Financial and Human Resource Costs
The financial implications of mentorship relationship failures extend far beyond the direct costs of program administration. Organizations face significant expenses related to employee turnover, reduced productivity, and the need for re-matching efforts when relationships fail. Studies indicate that effective mentoring programs can improve retention rates by 23% to 35%, suggesting that failed programs represent substantial opportunity costs in addition to direct financial losses.mentoringcomplete+3
The human resource implications are equally significant, with failed mentorship experiences often creating negative organizational cultures and reducing employee engagement with professional development initiatives. Research shows that employees involved in successful mentoring programs are promoted five times more often than those not involved in mentoring, while failed programs can actually hinder career advancement and create lasting negative associations with developmental opportunities.linkedin+3
Ripple Effects on Organizational Culture
Failed mentorship programs create ripple effects that extend throughout organizational culture, influencing employee perceptions of leadership commitment to development, fairness in opportunity allocation, and overall organizational effectiveness. When mentoring relationships fail publicly or repeatedly, they can create skepticism about other developmental initiatives and reduce overall employee engagement with professional growth opportunities.apa+3
The reputational impact on organizations can be particularly severe when mentorship failures involve issues of discrimination, harassment, or other ethical violations. These incidents can damage employer branding, complicate recruitment efforts, and create legal liabilities that extend far beyond the immediate mentoring relationship.qooper+2
Prevention and Intervention Strategies
Enhanced Matching Protocols
Research consistently demonstrates that effective matching represents the most critical factor in preventing mentorship relationship failures. Organizations are increasingly adopting sophisticated algorithmic approaches that consider multiple dimensions of compatibility, including personality traits, communication styles, career goals, and values alignment.tenthousandcoffees+3
The most successful matching protocols incorporate both quantitative assessments and qualitative evaluation processes, often including trial periods or structured introductory phases that allow both parties to assess compatibility before committing to long-term relationships. These approaches recognize that effective mentoring requires genuine personal connection and mutual respect that cannot be manufactured through purely administrative processes.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih+2
Comprehensive Training and Support Systems
The dramatic improvement in success rates when both mentors and mentees receive proper training—from 33% with no training to 90% with comprehensive preparation—underscores the critical importance of systematic skill development. Effective training programs address communication skills, goal-setting processes, feedback mechanisms, boundary management, and conflict resolution strategies.sbm+2
Ongoing support systems, including regular check-ins, peer networks for mentors and mentees, and access to program administrators for guidance, significantly improve relationship sustainability and satisfaction. Organizations that provide continuous support report substantially higher success rates and fewer premature relationship terminations.sfgmentornet+3
Cultural and Structural Reforms
Addressing systemic causes of mentorship failure requires comprehensive organizational culture change that values mentoring as a core leadership competency rather than an optional add-on activity. This includes incorporating mentoring effectiveness into performance evaluations, providing adequate time allocation for mentoring activities, and recognizing successful mentoring contributions through formal reward systems.pushfar+3
Structural reforms often involve redesigning program governance, establishing clear escalation procedures for addressing relationship problems, and creating accountability mechanisms that ensure program objectives are met. Organizations that treat mentoring as a strategic organizational capability rather than an HR program report significantly better outcomes and lower failure rates.mentoringcomplete+3
Future Directions and Emerging Solutions
Technology-Enhanced Matching and Support
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are increasingly being deployed to improve mentorship matching accuracy and provide ongoing relationship support. These systems can analyze communication patterns, identify early warning signs of relationship stress, and recommend interventions before problems become irreparable.fastcompany+1
Virtual and augmented reality technologies are also being explored as tools for enhancing remote mentoring relationships, providing immersive environments for collaboration and reducing some of the communication barriers associated with traditional digital platforms. These technological solutions show promise for addressing some of the logistical challenges that contribute to mentorship mismatches.chronus
Personalized Development Approaches
The future of effective mentorship increasingly involves personalized approaches that recognize individual learning styles, career objectives, and personal circumstances. This includes flexible program structures that can accommodate varying levels of intensity, different communication preferences, and diverse career trajectories.pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih+1
Organizations are also exploring multi-mentor models that provide mentees with access to different types of guidance and reduce the risk of single-point-of-failure relationships. These approaches distribute mentoring responsibilities across multiple individuals, reducing pressure on any single relationship and providing mentees with diverse perspectives and support networks.polishedresume+1
Conclusion
Mentorship relationship mismatches represent a complex, multifaceted challenge that requires sophisticated understanding and systematic intervention to address effectively. The evidence clearly demonstrates that while mentoring has tremendous potential to drive professional development and organizational success, poorly executed programs can actually harm participants and organizations. The key to success lies in recognizing that effective mentoring requires careful attention to matching processes, comprehensive training and support systems, and organizational cultures that genuinely value and support developmental relationships.
The research consistently shows that mentorship failures are not inevitable but are instead predictable outcomes of systematic deficiencies in program design, implementation, and support. Organizations that invest in proper matching protocols, comprehensive training, ongoing support, and cultural alignment report dramatically higher success rates and substantial returns on their mentoring investments.mentoringcomplete+3
As the workplace continues to evolve, with increasing emphasis on employee development, retention, and engagement, the importance of effective mentorship programs will only continue to grow. Organizations that can successfully address the challenges of mentorship mismatches will gain significant competitive advantages in talent development, employee satisfaction, and organizational performance. Those that fail to address these challenges will continue to experience the costly consequences of failed relationships and missed developmental opportunities.lifescied+1
The path forward requires commitment to evidence-based approaches, investment in proper resources and support systems, and recognition that effective mentorship is not a casual or incidental activity but rather a strategic organizational capability that requires dedicated attention and expertise to execute successfully. With proper attention to these factors, organizations can transform mentorship from a source of frustration and failure into one of their most powerful tools for developing talent and driving sustained success.
- https://www.mentoringcomplete.com/7-common-challenges-in-mentoring-relationships/
- https://www.linkedin.com/advice/3/how-can-you-avoid-common-mentor-mentee-conflicts-skills-mentoring
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3665769/
- https://www.pushfar.com/article/6-common-challenges-when-initiating-a-mentoring-programme/
- https://www.mentorcliq.com/blog/mentorship-programs-that-dont-work
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8490489/
- https://lead-true.com/lead-true-blog/why-mentorship-fails-individual
- https://projectskillsmentor.com/mentoring/mentoring-in-difficult-situations
- https://www.qooper.io/blog/mentor-mentee-matching-mistakes-to-avoid
- https://www.sbm.org/publications/outlook/issues/fall-2023/your-mentor-has-feelings-too-why-the-mentor-mentee-relationship-fails/full-article
- https://www.csescienceeditor.org/article/benefits-and-challenges-of-mentoring-in-cse-and-beyond/
- https://chronus.com/blog/why-workplace-mentorship-programs-fail
- https://www.linkedin.com/advice/0/what-most-common-reasons-mentorship-relationships-0bolf
- https://www.tenthousandcoffees.com/blog/mentoring-challenges-and-solutions
- https://www.womentech.net/blog/6-common-challenges-in-mentoring-relationships
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23165266/
- https://mentorloop.com/blog/mentoring-program-challenges/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3476480/
- https://mentorloop.com/blog/7-reasons-mentoring-programs-fail/
- https://chronus.com/blog/challenges-manual-mentoring-programs
- https://www.sfgmentornet.com/effective-communication-in-mentoring/
- https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/optimizing-success/202411/toxic-mentorship-mentor-or-tormentor
- https://www.evidencebasedmentoring.org/navigating-the-ocean-leveraging-the-big-five-personality-traits-for-effective-mentor-mentee-matching/
- https://www.mentoringcomplete.com/setting-the-foundation-for-a-quality-mentoring-relationship/
- https://www.fastcompany.com/90873314/6-signs-youve-got-a-toxic-mentor
- https://www.apa.org/gradpsych/2005/01/mentor-sticky
- https://www.mentorink.com/blog/3-factors-for-better-communication-in-mentoring/
- https://www.togetherplatform.com/blog/toxic-mentor
- https://www.togetherplatform.com/blog/getting-a-good-mentor-match
- https://www.linkedin.com/advice/3/what-most-common-sources-conflict-mentoring
- https://www.mentorcliq.com/blog/mentor-mentee-relationship-guide
- https://polishedresume.com/the-red-flags-of-a-toxic-mentor-most-people-miss/
- https://faculty-inclusive-mentoring.cornell.edu/grad-ed/core-mutual-expectations-graduate/conflict-resolution/
- https://eller.arizona.edu/news/2022/07/8-tips-maintain-good-mentormentee-relationship
- https://www.utmb.edu/news/article/utmb-news/2023/04/18/6-signs-you-ve-got-a-toxic-mentor
- https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/education/articles/10.3389/feduc.2023.1198094/pdf
- https://hbr.org/2023/06/a-better-approach-to-mentorship
- https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=1d8eb38a05e8ce7c5a98deddb010daab69a80f84
- https://www.lifescied.org/doi/10.1187/cbe.23-05-0070
- https://www.mentorink.com/blog/challenges-in-mentoring-programs-and-how-to-mitigate/
- https://interruptdelivers.com/themash/embedded-mentorship
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0149206399800683/pdf?md5=8499fb6eac87a0c624e1d23913efff63&pid=1-s2.0-S0149206399800683-main.pdf
- https://www.togetherplatform.com/blog/how-to-boost-employee-participation-in-your-mentorship-program
- https://ccc.bc.edu/content/ccc/blog-home/2024/01/mentoring-in-workplace-examples-best-practices.html
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0738081X11001490
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666602221000173
- https://www.togetherplatform.com/blog/common-mentoring-challenges
- https://www.mentoringcomplete.com/measuring-mentorship-success-key-metrics-and-evaluation-strategies/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2352144/
- https://www.rte.ie/brainstorm/2018/1004/1000906-how-peer-mentoring-is-reducing-student-dropout-rates/
- https://www.mentorink.com/blog/mentoring-statistics/
- https://www.mentorcliq.com/blog/mentoring-stats
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/value-mentoring-proven-benefits-data-driven-insights-d2wtf
- https://www.scirp.org/journal/paperinformation?paperid=94944
- https://chronus.com/blog/mentoring-statistics
- https://www.aihr.com/blog/mentorship-programs/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40033134/
- https://artofmentoring.net/the-common-pitfalls-in-mentoring-programs/
- https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/education/articles/10.3389/feduc.2023.1156725/pdf
- https://www.evidencebasedmentoring.org/new-research-identifies-five-reasons-mentoring-relationships-end/
- https://guider-ai.com/blog/mentoring-statistics-the-research-you-need-to-know/
- https://www.redalyc.org/journal/6137/613777779004/html/
- https://mentorloop.com/blog/mentoring-statistics/
- https://www.tenthousandcoffees.com/blog/how-to-measure-the-success-of-corporate-mentorship-programs
- https://www.people360ai.com/blog/what-to-do-if-theres-a-bad-mentoring-match
- https://www.entrepreneur.com/leadership/how-i-failed-as-a-mentor/286293
- https://www.togetherplatform.com/blog/workplace-mentoring-program-best-practices
- https://radicalmentoring.com/six-reasons-mentors-tell-failure-stories/
- https://www.linkedin.com/advice/0/how-do-you-deal-potential-mentoring-gaps-mismatches-your
- https://www.linkedin.com/posts/ravbumbra_why-your-mentorship-program-isnt-working-activity-7213637873357463553-4mYh
- https://partners.imentor.org/help/4-case-studies-of-challenging-pairs
- https://www.mentorcliq.com/blog/lessons-learned-through-failure
- https://www.togetherplatform.com/blog/mentorship-program-mistakes
- https://mentorloop.com/blog/6-common-mentoring-challenges-solutions/
- https://hbr.org/2024/12/why-mentoring-programs-fail-and-how-to-make-them-worthwhile